







|
|
cDNA Spot Segmentation
Image processing techniques such as denoising,
enhancement, data normalization, and spot localization, usually precede the
image segmentation step which is considered the most important processing
operation to be performed prior the determination of the gene expressions.
Image segmentation refers to partitioning an image into different regions
that are homogeneous with respect to some image feature. Assuming that the
pixels with the same feature characteristics constitute meaningful regions
such the microarray spots, the problem reduces to pixel classification.
Since under the ideal conditions each spot has its own unique magnitude and
directional characteristic, uniformity in vector magnitude and
directionality can be used as the criterion for partitioning the cDNA vector
field into disjoint regions corresponding to distinguishable spots.
| |
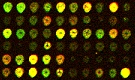
Acquired cDNA image |
|
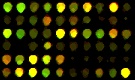
Segmented spots |
|
|
The
segmentation can be performed by achieving root signals of a nonlinear
vector filtering operator which uses simultaneously both the magnitude and directional
characteristics of the cDNA vectorial inputs during processing and outputs one of the vectorial
inputs inside a processing window as the result of the filtering
operation. In this way, the filtering process
converges within a few iterations to a root signal, which is not
further affected by the processing filter. The repetitive use of an
operator capable of normalizing the data population emphasizes the
most dominant cDNA vectors in localized neighborhoods. Thus, the
generated root signal represents the segmented microarray image with
the regular spots ideally separated from the background. Moreover,
during its convergence phase such a cDNA image processing solution simultaneously denoises, enhances, normalizes data, rejects irregular spots, and
automatically segments spots from the background. Combined with an
additional module which thresholds the magnitude of the root signal,
the approach can remove residual, irregular foreground information
and enhance perceived and measured differences between foreground
and background information in the segmented image. |
|
References: |
|
 | R. Lukac and K.N. Plataniotis, "cDNA Microarray
Image Segmentation Using Root Signals," International
Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, vol. 16, no. 2,
pp. 51-64, April 2006. |
|
|
|
