







|
|
cDNA Spot Localization
cDNA spot localization solutions use the cDNA microarray
image as the input and transforms it into an edge map which can be viewed as
a line drawing image with a spatial resolution identical to that of the
input. An intensity edge map corresponds to sudden changes in image
characteristics which tend to occur at spot boundaries and the locations of
these changes reflect the shapes of cDNA spots.
| |
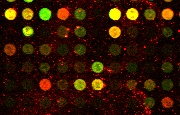
Acquired cDNA image |
|
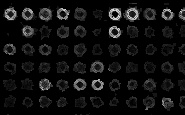
Localized spots |
|
|
Multichannel images such as cDNA microarray images
carry information contained in the various spectral channels. This
information can be used to identify and detect spot edges. The
boundary between two surfaces with different properties can be
determined in more than one way, as the edge formation can be
attributed to changes in one channel or in both channels
simultaneously. Since cDNA images can be viewed as vector fields,
edges can potentially be detected as differences in local
vector statistics which accurately reflect variations in spectral
information and spatial image content. Moreover, due to the
utilization of the robust order-statistic principle, the nonlinear
vector operators can be less sensitive to noise compared to the
conventional edge operators such as Sobel, Prewitt, and Canny edge
detectors. |
|
References: |
|
 | R. Lukac and K.N. Plataniotis: A Taxonomy of Color
Image Filtering and Enhancement Solutions. In Advances in Imaging
and Electron Physics, (ed.) P.W. Hawkes, Elsevier/Academic
Press, vol. 140, pp.187-264, June 2006. |
 | R. Lukac, B. Smolka, K. Martin, K.N.
Plataniotis, and A.N. Venetsanopoulos, "Vector Filtering for Color
Imaging," IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, Special
Issue on Color Image Processing, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 74-86, January 2005. |
 | R. Lukac, K.N. Plataniotis, B. Smolka, and A.N.
Venetsanopoulos, "A Multichannel Order-Statistic Technique for
cDNA Microarray Image Processing," IEEE Transactions on NanoBioscience,
vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 272-285, December 2004. |
|
|
|
