







|
|
cDNA Data Normalization
Since the noisy samples deviate from other samples in a given data
population, the normalization operation should minimize systematic
variations (attributed to noise) in the cDNA image measurements, enhance
spot localization, and emphasize biological differences between the
experimental and control population. To achieve the objective and simultaneously preserve the
structural content of the image, local vector filtering operators should be
used. These multichannel data-normalizing oprators are designed to replace
the corrupted cDNA vectorial input most centrally located in a finite area
of support with the vector which is statistically closest to all members
within the area of support.
| |
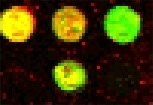
Real cDNA image |
Using robust vector order-statistics, the
ordering of the aggregated distances or similarity functions calculated
between cDNA vectors located inside the processing window identifies the
outlying observations and allows for the smoothing of the cDNA vectors'
population.
|

Normalized cDNA image |
|
| |
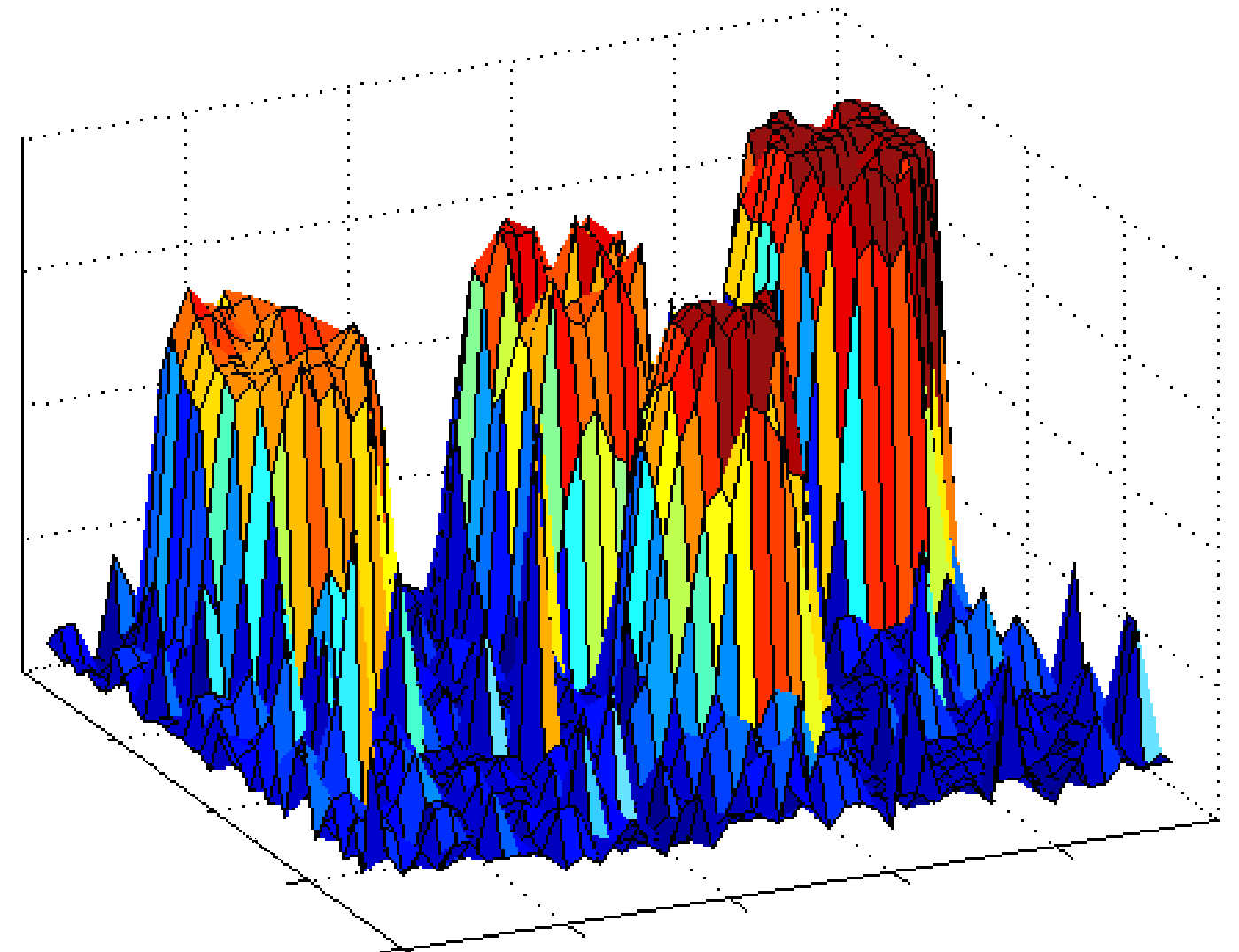
Magnitude characteristics of the real cDNA image |
|
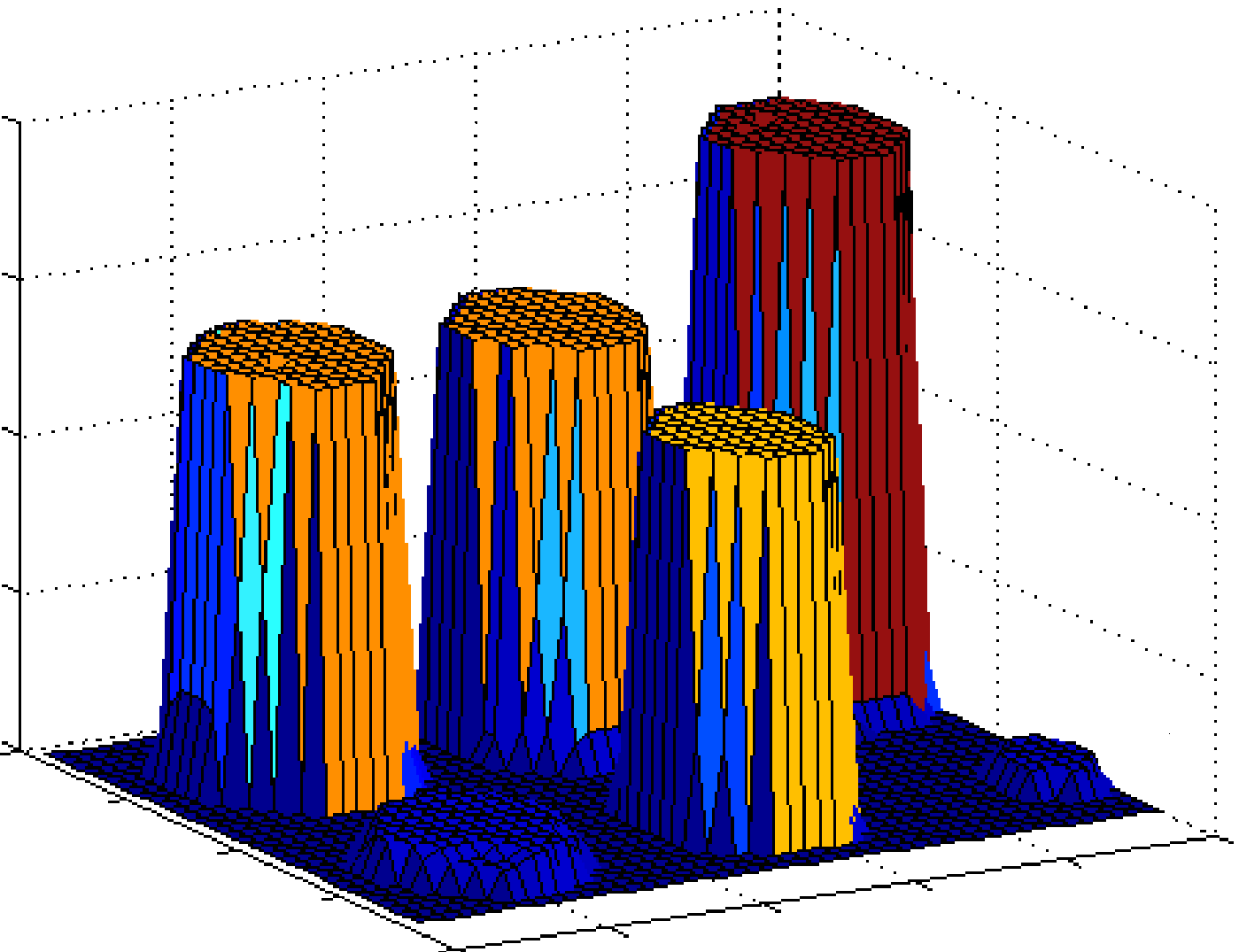
Magnitude characteristics of the normalized image |
|
| |
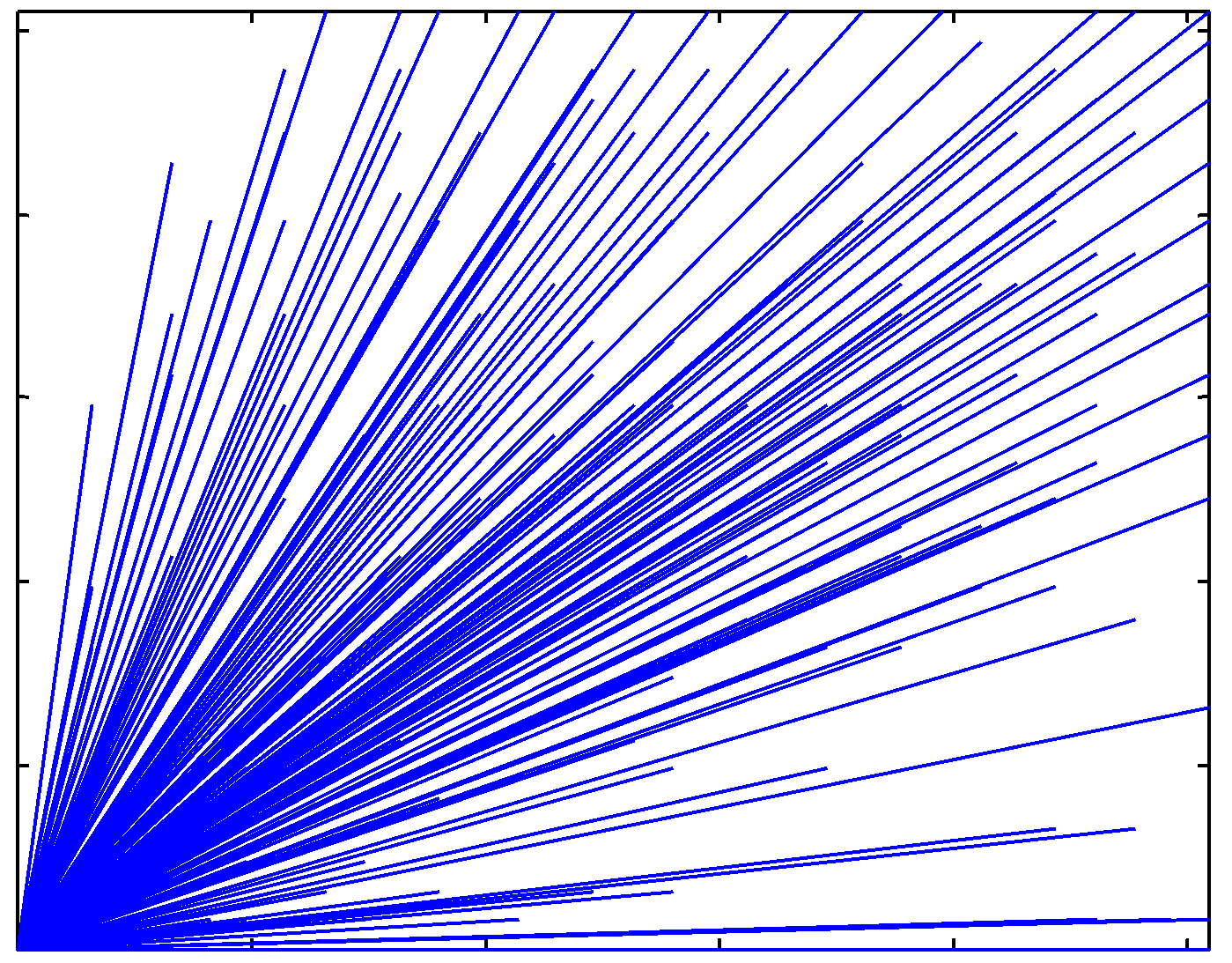
Directional characteristics of the real cDNA image |
|
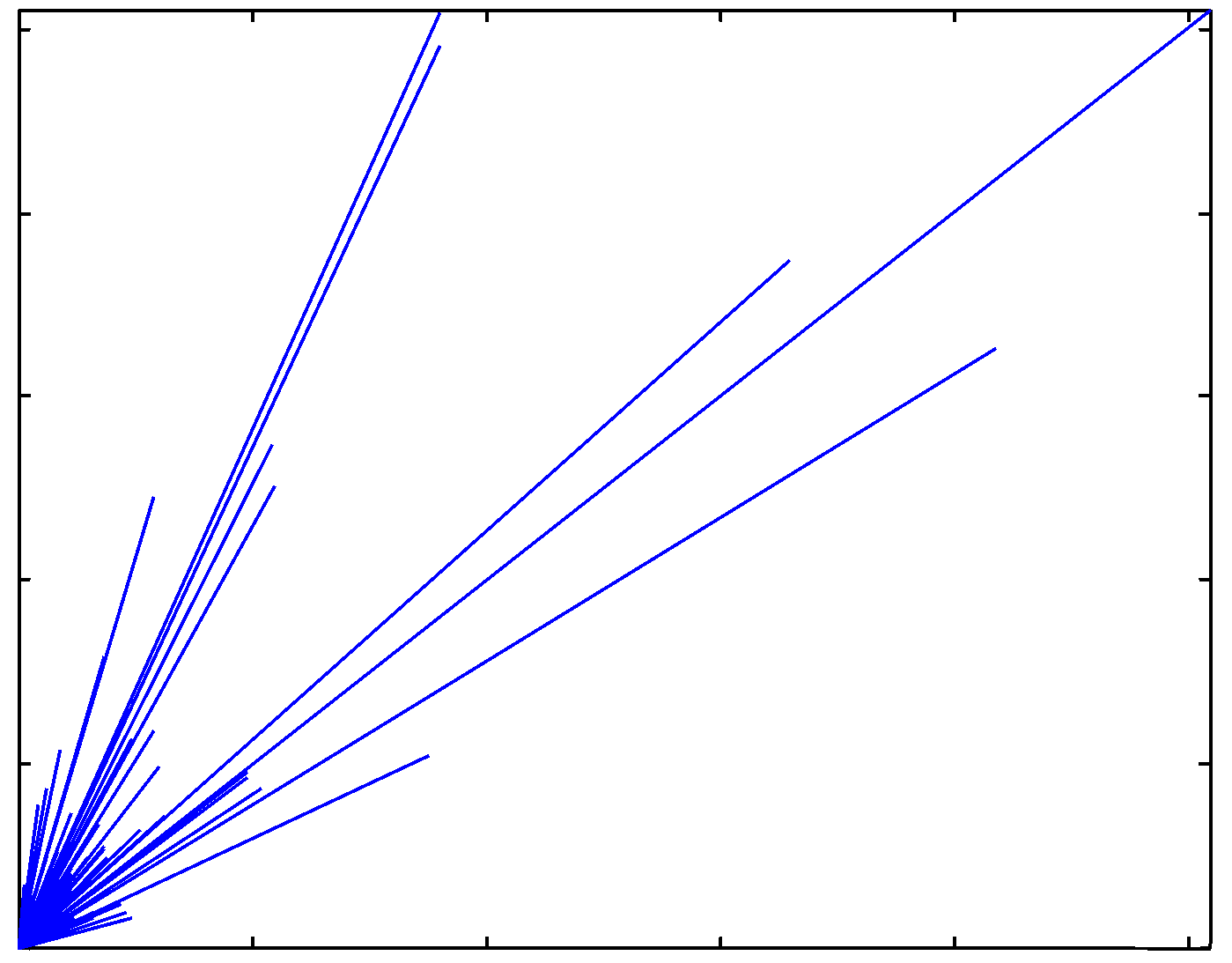
Directional characteristics of the normalized image |
|
|
The cDNA vector minimizing the aggregated distance or
maximizing the vector similarity criterion to other samples within
the processing window is the most representative to the whole
windowed set. Therefore, the choice of the sample associated with
the minimum aggregated distance value is critical for the proper
normalization of the image data. Using vector filtering operators
which are selective in nature and use the minimization principle to
determine the output, the noisy samples do not contribute to the
filter output. This makes the cDNA data normalization approach
robust to microarray image noise while it allows for preserving the
structural content of the acquired cDNA image. The normalized cDNA
image data should exhibit uniformity in the characteristics of the
cDNA vectors. The same feature can be used as the base for
microarray spot localization and image segmentation. |
|
References: |
|
 | R. Lukac and K.N. Plataniotis, "cDNA Microarray
Image Segmentation Using Root Signals," International
Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, vol. 16, no. 2,
pp. 51-64, April 2006. |
 | R. Lukac, K.N. Plataniotis, B. Smolka, and A.N.
Venetsanopoulos, "cDNA Microarray Image Processing Using Fuzzy
Vector Filtering Framework," Fuzzy Sets and Systems, Special Issue on Fuzzy Sets and Systems in Bioinformatics,
vol. 152, no. 1, pp.17-35, May 2005. |
 | R. Lukac, B. Smolka, K. Martin, K.N.
Plataniotis, and A.N. Venetsanopoulos, "Vector Filtering for Color
Imaging," IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, Special
Issue on Color Image Processing, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 74-86, January 2005. |
 | R. Lukac, K.N. Plataniotis, B. Smolka, and A.N.
Venetsanopoulos, "A Multichannel Order-Statistic Technique for
cDNA Microarray Image Processing," IEEE Transactions on NanoBioscience,
vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 272-285, December 2004. |
|
|
|
